Scientific Results
- Positions for CIG galaxies
- Redshift and distances
- Morphologies
- Isolation
- A catalogue of neighbours around isolated galaxies based on POSS I & II images
- Quantification of isolation based on POSS I & II images
- Revision of isolation criteria using the SDSS
- Effects of the environment on galaxies in the..
- Catalogues of isolated galaxies, isolated pairs, and isolated triplets..
- Star formation
- Optical specialization
- Radio continuum properties
- Atomic gas
- Isolated Galaxies
- Environment and faint features of CIG 96: deep optical and HI observations (2018)
- Atomic gas scaling relations (2018)
- A ∼12 kpc HI extension and other HI asymmetries in the isolated galaxy CIG 340 (2014)
- HI asymmetry in the isolated galaxy CIG 85 (2012)
- HI asymmetries in the isolated galaxy CIG 292 (2011)
- Asymmetries in isolated galaxies (2011)
- The large asymmetric HI envelope of CIG 96 (2005)
- Compact groups
- Studies of complementary samples
- Isolated Galaxies
- Molecular gas
- Nuclear activity
We have performed a detailed photometric analysis (bulge-disk-bar decomposition and Concentration-Asymmetry-Clumpiness – CAS parametrization) for Sb-Sc morphological types of AMIGA sample, as they are the most representative population among the isolated spiral galaxies.
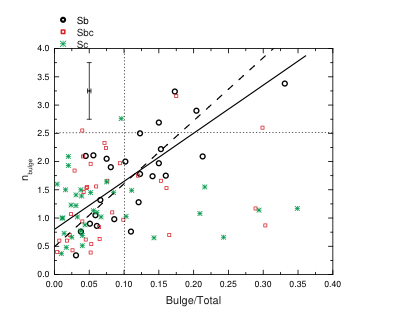
Our analysis yields a large number of important galactic parameters and various correlation plots are used to seek relationships that might shed light on the processes involved in determining those parameters. Assuming that the bulge Sérsic index and/or Bulge/Total luminosity ratios are reasonable diagnostics for pseudo- versus classical bulges, we conclude that the majority of late-type isolated disk galaxies likely host pseudobulges rather than classical bulges.
Our parametrization of galactic bulges and disks suggests that the properties of the pseudobulges are strongly connected to those of the disks. This may indicate that pseudobulges are formed through internal processes within the disks (i.e. secular evolution) and that bars may play an important role in their formation. Although the sample under investigation covers a narrow morphological range, a clear separation between Sb and Sbc-Sc types is observed in various measures, e.g. the former are redder, brighter, have larger disks and larger bars, more luminous bulges, are more concentrated, more symmetric and clumpier than the latter. A comparison with samples of spiral galaxies (within the same morphological range) selected without isolation criteria reveals that the isolated galaxies tend to host larger bars, are more symmetric, less concentrated and less clumpy.